Up to 24 cash back Explanations of why the population is growing or declining in some places are based on patterns and trends in fertility mortality and migration. An environmental or cultural feature of the landscape that hinders migration some factor in a place that slows down migration Cyclic Movement.
Moving to a different state country or continent.

. Migration International migration is permanent movement from one country to another whereas internal migration is permanent movement within the same country. Most move short distance stay within own country 2. Ravensteins characteristics of migrants.
Regional Migration Patterns in the USA. Also to know is what is migration in human geography. What are the types of migration in geography.
Interregional migration is the movement from one region of a country to another. Stage 1 transhumancecyclical migrationseasonal migration. Rural settlement patterns are classified as clustered dispersed or linear.
Nomadic migration that has a closed route and is repeated annually or seasonally repetitive movement within the same places Migratory Movement. 3Stages 3 4 are the principle destinations for international migrants. Distribution - Density Concentration Pattern.
British economist Thomas Malthus coined the term overpopulation in the late 1700s. A change in the migration pattern in a society that results from industrialization population growth and other social and economic changes that also produce the demographic transition. Up to 24 cash back AP Human Geography.
Migration is the movement of people from one permanent home to another. Population and Migration 2019-2020 THE CULTURAL LANDSCAPE RUBENSTEIN 11TH ED. 3 Languages A language is a form of.
The movement within the same region of the country is called intraregional migration. What are the two most common types of intraregional migration. A migration in which an eventual long-distance relocation is undertaken in stages eg rural to central city residence through farm to small town to suburb to the major central city Circular Migration.
People who are forced to migrate from their home country and cannot return for fear of. Leaving one country to move to another. Human movement involving movement across international boundaries.
Migration is usually distinguished from mobility in general by conventions of spatial and temporal scale. A short definition for Migration Studies. AP Human Geography Cultural Patterns and Processes Building materials are more prominent in folk culture since it is based on the environment beliefs and construction.
The temporary movement of a migrant worker between home and host countries to seek employment. A change in residence intended to be permanent. This movement changes the population of a place.
Changed the cultural ethnic geography of the US Brazil Central America the Caribbean Beginning in 1788 tens of thousands of. Livestock is moved seasonally between one area of pasture and another livestock between highland and lowland pastures. Malthus suggested that the worlds population was growing faster than the rate of food production and as a result.
Human geography or anthropogeography is the branch of geography that is associated and deals with humans and their relationships with communities cultures economies and interactions with the environment by studying their relations with and. 7 About the AP Human Geography Course 7 College Course Equivalent 7 Prerequisites COURSE FRAMEWORK 11 Introduction 12 Course Framework Components 13 Course Skills 15 Course Content 18 Course at a Glance 21 Unit Guides 22 Using the Unit Guides 25 UNIT 1. 7 about the ap human geography course 7 college course equivalent 7 prerequisites course framework 11 introduction 12 course framework components 13 course skills 15 course content 18 course at a glance 21 unit.
A spatial pattern is a perceptual structure placement or arrangement of objects on Earth. Sacred places include direction because of cultural beliefs and are commonly used in China to see where walls doors and beds are placed. Population and Migration Patterns and Processes.
Human movement within a nation-state such as ongoing westward and southward movements in the United States. Population and Migration Notes January 17 2019 in AP Human Geography by admin. A pattern of regular seasonal movement by human groups.
It can be seen as a form of pastoralism or nomadism. What is a pattern in AP Human Geography. Thinking Geographically 37 UNIT 2.
Interregional migration is movement from one region of a country to another while intraregional migration is. The movement of groups and individuals from one place to another involving a change of usual residence. Moving back to where you came from.
International migrants may be voluntary or forced. Most migrants come from Stage 2 of the demographic transition model. Plus join AP exam season live streams Discord.
Up to 24 cash back AP Human Geography Exam 2001 2014 Categorized by topic below are all FRQ exams from 2001 2014. AP Human Geography. International Migration Patterns Global migration patterns reveal that most people migrate from developing countries to developed ones.
What is the definition of migration in geography. Human patterns of movement reflect the conditions of a changing world and impact the cultural landscapes of both the places people leave and the places they settle. Moving within a state country or continent.
International migrants are much less numerous than internal migrants. Impact on Economic Structure Friction of Distance and Age Structure of Population FRQ Scoring Guidelines 2008. The FRQ link connects to.
Migration Definition Ap Human GeographyImmigrants who come to a country to work and then move back to their home country with money. Up to 24 cash back Largest forced migration in history of humanity was the Atlantic slave trade from Africa estimates from 12-30 million people Slave trade did unimaginable damage to African societies. For example when learning about the relevance of place context and government policies students may analyze fertility rates and agesex structures shown in population pyramids in various countries.

Chapter 3 Key Issue 1 Migration Ap Human Geography Youtube

U S Internal Migration Ms Silvius S Ap Human Geography
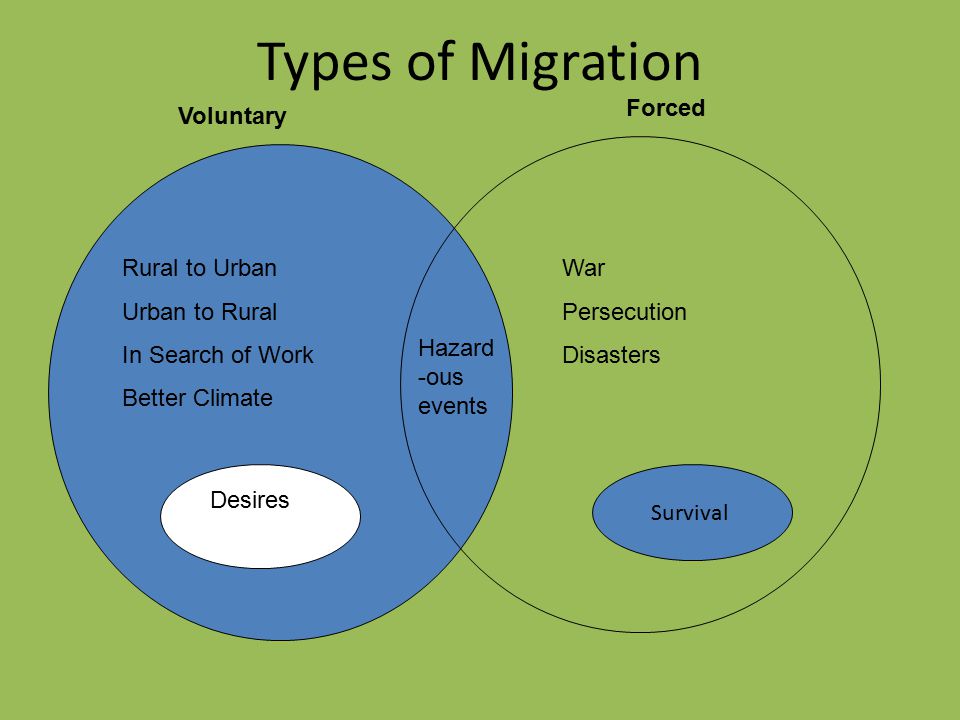
Causes Of Migration Ap Human Geography Ppt Video Online Download

Ap Human Geography Unit 2 Ppt Video Online Download

Migration Ap Human Geography Unit 2 Mobility Migration

Ap Human Geography Chapter 3 Flashcards Quizlet

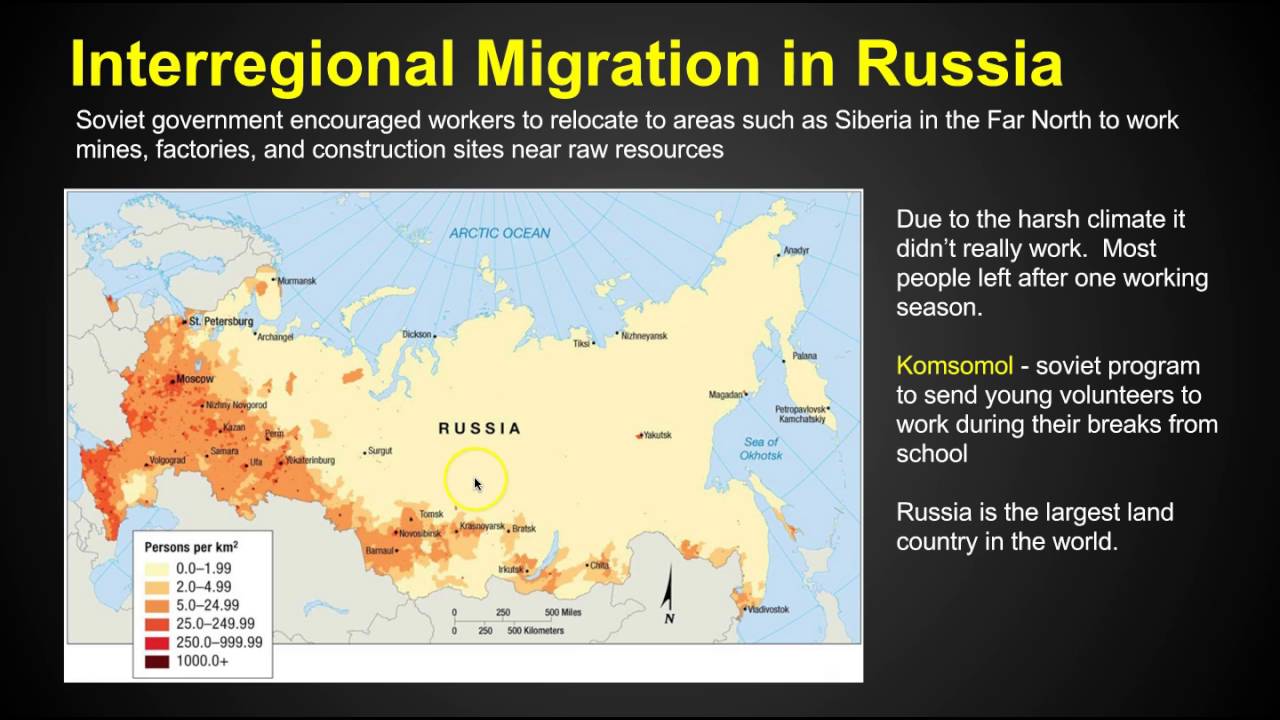
0 comments
Post a Comment